

DYCE assessment is based on MIDAS technology. The Multiple Intelligences Developmental Assessment Scales (MIDAS) was developed by Dr. C. Branton Shearer in 1987 as a tool to assess an individual's strengths across the Multiple Intelligences (MI) Theory proposed by Dr. Howard Gardner in 1983.
1. Inspired by Howard Gardner’s Theory (1983)
a. Dr. Howard Gardner, a developmental psychologist at Harvard University, introduced the Theory of Multiple Intelligences (MI) in his book Frames of Mind.
b. He proposed that intelligence is not a single entity (IQ) but consists of eight different types of intelligences (Linguistic, Logical-Mathematical, Musical, Bodily-Kinesthetic, Spatial, Naturalist, Interpersonal, Intrapersonal).
c. Later, an additional intelligence, Existential Intelligence, was suggested but is not officially included in MIDAS.
2. Creation of MIDAS (1987)
a. Dr. C. Branton Shearer, a psychologist and researcher, designed MIDAS to provide a structured method of evaluating a person’s multiple intelligences.
b. The assessment was created as a self-report questionnaire, collecting information about everyday activities, skills, and abilities.
MIDAS is based on Howard Gardner’s Theory of Multiple Intelligences (MI) and applies psychometric and cognitive science principles to assess individuals' unique intellectual strengths.
Theoretical Foundation: Gardner’s Multiple Intelligences Theory
Howard Gardner, a developmental psychologist at Harvard University, introduced the Multiple Intelligences (MI) Theory in 1983. His research challenged traditional IQ tests, arguing that intelligence is not a single ability, but rather consists of distinct cognitive capacities.
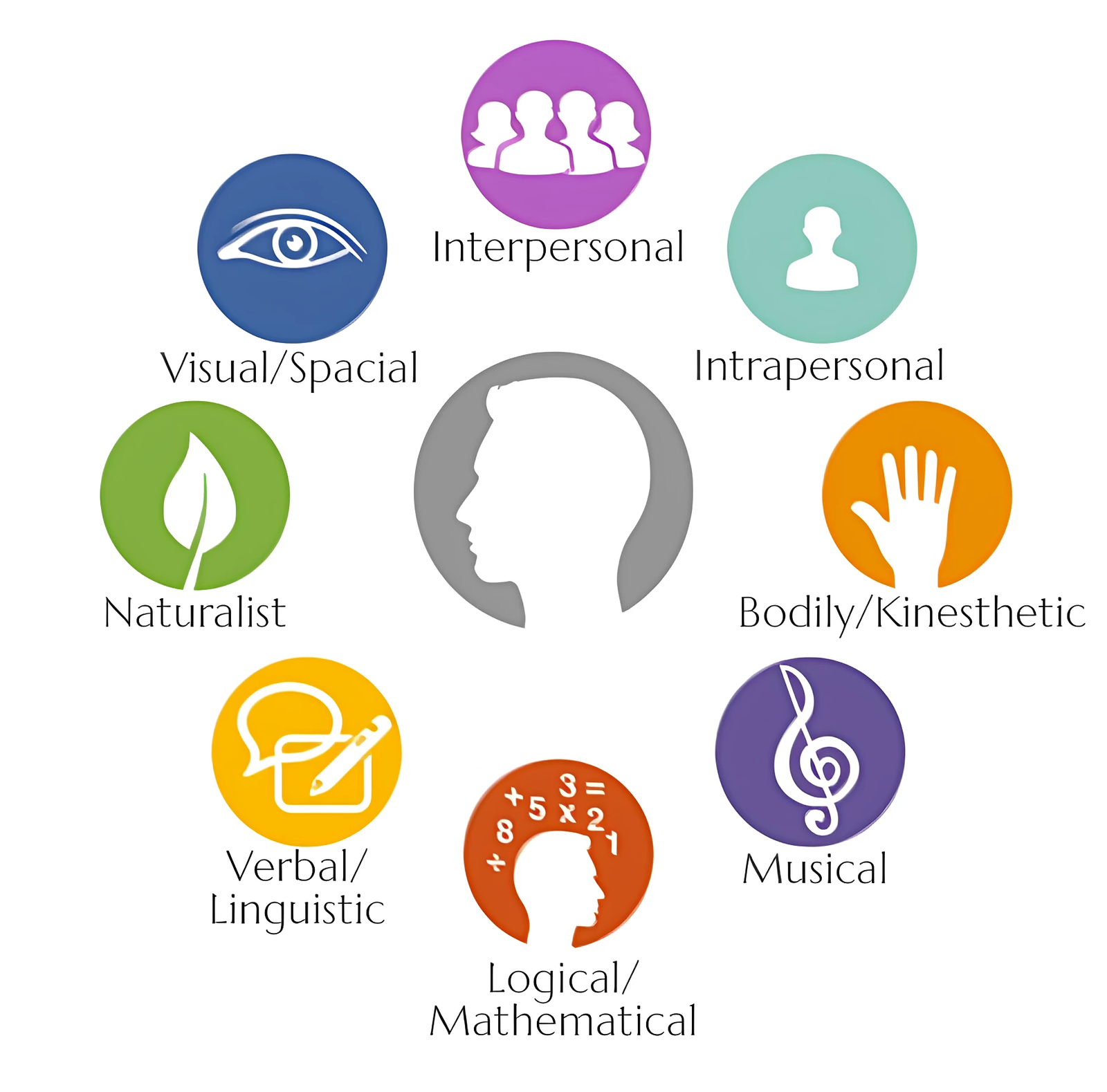
The Eight Core Intelligences in MIDAS
1. Linguistic: Language skills (reading, writing, storytelling, public speaking).
2. Logical-Mathematical: Problem-solving, pattern recognition, logical reasoning.
3. Musical: Sensitivity to sounds, rhythm, pitch, and melody.
4. Bodily-Kinesthetic: Physical coordination, dexterity, and movement-based learning.
5. Visual-Spatial: Ability to visualize, navigate, and understand spatial relationships.
6. Interpersonal: Understanding and interacting effectively with others.
7. Intrapersonal: Self-awareness, emotional intelligence, and reflection.
8. Naturalist: Sensitivity to nature, patterns in the environment, and categorization of objects.
MIDAS assesses these intelligences through a structured questionnaire and provides a scientifically backed profile of an individual's cognitive strengths.
MIDAS Assessment Structure: Psychometric Approach
Dr. C. Branton Shearer developed MIDAS in 1987 as a self-report inventory that gathers data about an individual's intelligence strengths through daily life activities and abilities.
How It Works:
a. The assessment consists of multiple-choice and Likert-scale questions (e.g., “How often do you engage in music-related activities?”).
b. Respondents self-report their experiences, interests, and habits in different areas of intelligence.
c. Answers are analyzed statistically to measure strengths and weaknesses in each intelligence type.
d. The results provide a personalized profile of intelligence distribution.
MIDAS is a scientifically designed assessment tool that helps individuals identify their unique intelligence strengths based on Howard Gardner’s Multiple Intelligences (MI) Theory. It is useful for students, professionals, educators, and organizations in various ways.
Career Guidance:
• MIDAS helps students discover which career paths align with their natural talents.
Personalized Learning:
• Schools and teachers can tailor teaching methods to suit a student's learning style.
Boosts Confidence & Motivation:
• Students feel more capable when they understand their strengths.
• Helps them focus on areas where they excel rather than struggling with conventional methods.
Helps in Job Selection:
• Professionals can choose roles that fit their intelligence strengths.
Enhances Skill Development:
• Identifies areas for growth and improvement based on intelligence profiles.
Leadership & Teamwork Enhancement:
• Organizations can use MIDAS to create effective teams based on diverse intelligences.
Personalized Teaching Strategies:
• Teachers can use MIDAS to adapt teaching methods based on students’ intelligence types.
Better Career Counseling:
• Helps counselors guide students based on scientific intelligence mapping rather than just interests.
Helps in Self-Understanding:
• MIDAS gives individuals a clear picture of their strengths and weaknesses.
Enhances Relationships & Communication:
• Understanding one's interpersonal and intrapersonal intelligence improves relationships.
Supports Life Decisions:
• Helps people choose activities, hobbies, and life goals that align with their intelligence profile.


• Students – for career guidance and academic success
• Job Seekers – to find the right career fit
• Working Professionals – to improve performance or switch careers
• Teachers & Counselors – to guide students effectively
• Parents – to support their child’s unique learning style
• HR & Employers – to optimize employee roles & productivity
• Anyone Seeking Self-Discovery – to understand strengths and make better life decisions